In relay manufacturing, the internal structure is highly compact, and components such as contacts, coils, magnetic circuits, plastic housings, and sealing elements are extremely sensitive to press-fit quality. In high-volume production—especially for automotive relays, household appliance relays, and telecom relays—traditional press machines (hydraulic, pneumatic, or mechanical cam presses) can no longer meet the requirements for consistency, traceability, and ultra-high precision.
This article analyzes six major pain points in relay press-fit assembly, their technical root causes, and how XIRO electric servo press machines provide a reliable, controllable, and traceable solution.

Intermediate Relay
(For confidentiality purposes, the product images shown are representative illustrations only and do not depict actual client-specific product)
1. Six Pain Points in Traditional Relay Press-Fit Assembly and Their Root Causes
Pain Point 1: Inaccurate Pressure Control Leading to Contact Damage
Case: At an automotive relay plant, contact components were damaged during press-fit. Due to hydraulic valve response delay and oil-line elasticity, the instantaneous pressure reached 150–180% of the set value, causing plastic deformation of silver alloy contacts and resulting in a 12% defect rate.
Root Causes:
1) Hydraulic response delay
Hydraulic valve spools have >100 ms reaction delay. During fast relay closure, they cannot adjust pressure in time, resulting in transient pressure spikes (e.g., 10 kN → 18 kN).
2) Temperature drift
Hydraulic oil temperature fluctuating ±15°C leads to ±8% pressure instability.
Traditional press machines lack real-time feedback and cannot compensate for viscosity-induced pressure deviation.
3) Soft contact materials
Silver-based contact materials have relatively low softness and melting points (~960°C). Localized over-pressure or heat accumulation causes surface collapse or “static sticking.”
Pain Point 2: Insufficient Displacement Accuracy Causing Seal Failure
Case: In a home appliance relay, press-fit depth deviation reached ±0.15 mm (tolerance ±0.1 mm). The silicone sealing ring compression ratio dropped to only 60–65%, resulting in an 18% failure rate in waterproof testing.
Root Causes:
1) Mechanical transmission chain errors
Ball screw backlash: 0.03–0.05 mm
Gear meshing clearance: 0.02–0.03 mm
Low-speed pressing creates cyclical micro-fluctuations (0.01–0.02 mm).
2) No displacement closed-loop control
Manual end-point calibration combined with screw nut wear (0.01 mm/month) leads to cumulative drift. This makes sealing ring compression unable to remain within the optimal 15–30%.
Pain Point 3: Long Changeover Time and Poor Production Flexibility
Case: A manufacturer switching models required mold replacement and limit adjustments. The process took 120 minutes, reducing equipment utilization below 60%.
Reasons:
Rigid mechanical structure requiring manual disassembly.
No parameter storage or recipe functionality; each product type must be re-tuned from scratch.
Pain Point 4: Difficulty in Quality Traceability
Case: A military-grade relay batch exhibited excessive contact resistance. Because only manual static readings were recorded (no pressure peak, hold time, or displacement curves), the root cause could not be traced. The entire batch was scrapped.
Reasons:
No high-frequency data acquisition
No force-displacement curve
No SPC capability
Cannot identify whether defects came from pressure overshoot or depth deviation
2. XIRO Electric Servo Press Machines Technical Solutions
Modern electric servo press machines (servo press, precision press machine) overcome the inherent limitations of hydraulic or pneumatic presses through real-time closed-loop control, multi-stage press-fit modes, and full-process data traceability.
1. Dynamic Closed-Loop Pressure Control (Solving Pressure Inaccuracy)
1) High-precision sensor network
1 kHz strain-gauge pressure sampling
Direct torque control through servo motor
Pressure accuracy: ±0.5% FS
Response time: <10 ms
Result: Pressure fluctuation reduced from ±8% to ±0.7%, eliminating contact deformation defects.
2) PID + Feedforward Composite Algorithm
The servo press machine uses a predictive and corrective hybrid approach:
PID control ensures stable force output and eliminates steady-state error.
Feedforward control predicts deformation behavior based on displacement speed, preventing contact “impact.”
Overshoot <5% under relay small-stroke conditions.
Adaptive gain adjusts based on contact material modulus (70–90 GPa for silver alloys).
2. High-Accuracy Linear Scale Feedback (Solving Depth Accuracy Issues)
1) Nanometer-level feedback
μm resolution linear scale
1–2 MHz signal output
Feedback delay <1 μs
Effective removal of screw backlash and transmission errors
2) Force–Displacement Composite Control
Fast approach: 50 mm/s
Auto-switch to force+position control upon contact
Depth accuracy ±0.01 mm
3) Elastic deformation compensation
Embedded database for seal materials:
Silicone (E = 0.5–3 MPa)
Fluoro-rubber
PU elastomers
Automatically compensates compression to maintain final depth accuracy within ±0.02 mm.
Temperature compensation ensures <0.01 mm deviation even under ±15°C ambient change.
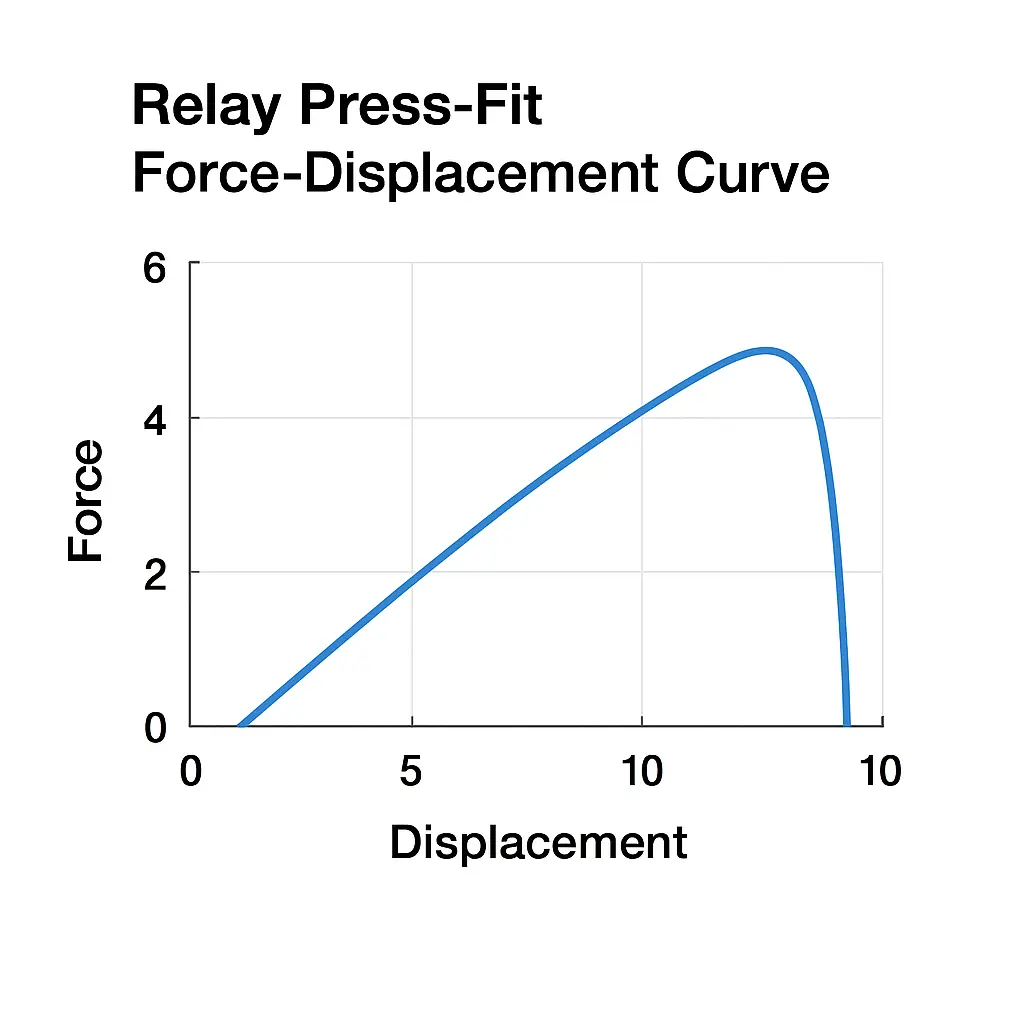
Relay press-fit force–displacement curve
(Source: XIRO )
3. Parameterized Quick Changeover (Improving Process Flexibility)
1) Recipe management system
SQL-based parameter storage
100+ press-fit recipes
Includes force-speed-displacement curves, hold time, thresholds
QR-code quick loading (<0.5 s)
2) Precision quick-change tooling
Pneumatic locking + taper positioning
Changeover time <2 minutes
Positioning repeatability ±0.01 mm
4. Full-Process Quality Traceability
1) High-density data acquisition
Pressure: 1 kHz
Displacement: 0.1 μm resolution
Force-displacement-time 3D curve
100 sampling points/mm (traditional: 5 pts/mm)
2) Industrial IoT integration
OPC UA connection to MES
Automatic CPK/PPK generation
Real-time alarm for abnormal force/displacement
Supports ERP cost analysis and quality traceability
Conclusion
Relay press-fit assembly is a high-precision process featuring short stroke, low force, strict sealing requirements, and ultra-high consistency demands. Traditional hydraulic or pneumatic press machines lack the responsiveness, accuracy, flexibility, and data traceability required for modern relay manufacturing.
XIRO Electric servo press machines—equipped with closed-loop force control, nanometer-level position feedback, multi-stage press-fit modes, recipe management, and full digital traceability—completely eliminate the six major pain points of traditional relay press-fit processes.
They achieve:
Pressure accuracy: ±0.5% FS
Depth accuracy: ±0.01 mm
Seal compression consistency improved by 300%
Defect rate: 0 ppm
Changeover time: 120 min → 2 min
Traceability rate: 100%
For automotive, household, and high-reliability relay manufacturers, the electric servo press machine is becoming the standard equipment for improving yield, reliability, and process transparency.






